Star Log
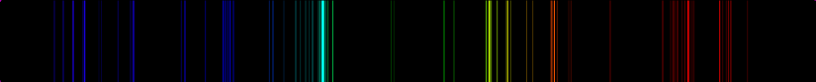
Chemical Make-Up:
Iron Abundance - (Fe/H = 0.0)
Carbon Abundance - (C/H = -0.4) Nitrogen Abundance - (N/H = +0.4) Oxygen Abundance - (O/H = -0.2) Over abundance of Nitrogen |
Location in Space:
434 light-years from the Sun27’09” (0.4525 Degrees) off North |
Stellar Classification:
F-G supergiants |
Photographs:
   |
References
EarthSky. (n.d.). Polaris is the North Star. Retrieved from http://earthsky.org/brightest-stars/polaris-the-present-day-north-star
The Emission Spectra of Various Atoms. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.astronomy.ohio-state.edu/~pogge/Ast350/Labs/Lamps/
Harvard. (n.d.). The chemical composition of Polaris. Retrieved from http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1986PASP...98..442L
Universe Today. (n.d.). What Are The Most Famous Stars? Retrieved from http://www.universetoday.com/45775/famous-stars/
|
No comments:
Post a Comment